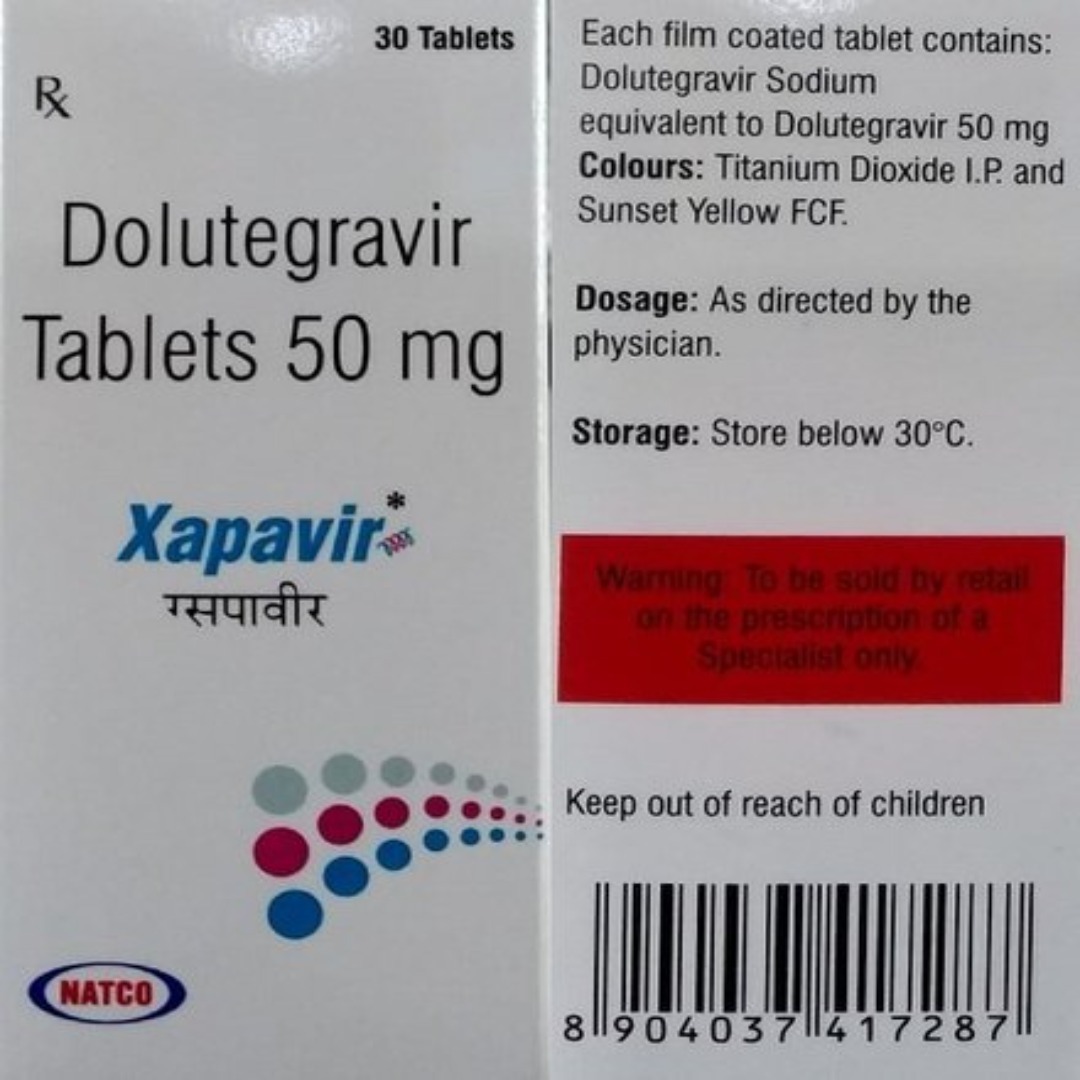
XAPAVIR INFORMATION
XAPAVIR is an antiretroviral medication that is used to treat HIV infection. XAPAVIR aids in the prevention of AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) and other HIV-related illnesses including cancer and dangerous infections. When administered as a daily therapy in conjunction with safe sex, XAPAVIR helps to reduce the risk of HIV-1 infection.
XAPAVIR is a medication that is made from Dolutegavir 50 mg. XAPAVIR acts by interfering with the function of the nucleotide and nucleoside reverse transcriptase enzymes, which are required for viral replication. XAPAVIR , when taken together, aids in the treatment of HIV infection.
PrEP stands for pre-exposure prophylaxis.
Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis, or PrEP, is a frequent term for this drug. What is a PrEP, exactly? PrEP (pre-exposure prophylaxis) is a treatment that HIV-positive persons take to avoid infection via sex or injectable drug usage. PrEP is a very effective HIV prevention tool when used as directed. The word usually refers to the use of antiviral medications as part of an HIV/AIDS preventive strategy. PrEP is one of a variety of HIV prevention treatments for persons who are HIV-negative but have a greater risk of contracting the virus, such as sexually active adults, those who use injectable drugs, and serodiscordant sexually active couples.
What is the efficacy of PrEP? PrEP, or pre-exposure prophylaxis, is a very efficient HIV prevention tool. When taken as directed, PrEP decreases the risk of contracting HIV via intercourse by nearly 100%. Although there is less data on how effective PrEP is in persons who inject drugs, we do know that when taken as directed, PrEP decreases the risk of HIV infection by at least 74%. When PrEP is not taken as directed, it has a substantially lower effectiveness.
XAPAVIR should be taken with meals. XAPAVIR should be swallowed whole with water, not chewed or crushed. Depending on your medical condition, you should take XAPAVIR for as long as your doctor has recommended it. Certain typical adverse effects, such as headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, weakness, and rash, may occur in certain situations. The majority of these adverse effects do not necessitate medical treatment and will subside with time. However, if you are experiencing these adverse effects on a regular basis, you should consult your doctor.
XAPAVIR does not prevent the transmission of HIV infection, therefore practice safe sex and take the required measures. If you are pregnant or intend to become pregnant, speak with your doctor. XAPAVIR should not be taken during nursing. XAPAVIR can make you dizzy, so drive carefully. Children under the age of 12 should not consume XAPAVIR . To avoid any negative effects or interactions, keep your doctor informed about your health condition and the medications you’re taking.
HIV infection PrEP XAPAVIR uses

Medicinal Advantages
XAPAVIR is an antiretroviral medication that is used to treat HIV infection. XAPAVIR aids in the prevention of AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) and other HIV-related illnesses including cancer and dangerous infections. XAPAVIR is a medication that combines two drugs: emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil. Tenofovir disoproxil is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor and Emtricitabine is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor. XAPAVIR acts by interfering with the function of the nucleotide and nucleoside reverse transcriptase enzymes, which are required for viral replication. XAPAVIR , when taken together, aids in the treatment of HIV infection. XAPAVIR , in combination with safe sex practices and lifestyle modifications, may minimize the risk of contracting HIV or spreading it to others.
Use Instructions
XAPAVIR should be taken with meals. XAPAVIR should be swallowed whole with water, not chewed or crushed. Your doctor will determine how long you should take XAPAVIR based on your medical condition.
Storage
Store in a cool, dry location away from direct sunlight.
XAPAVIR Side Effects
Headache \sDizziness
Nausea
Vomiting \sDiarrhoea
Weakness
Rash
Drug Recommendations
If you are allergic to any of the ingredients in XAPAVIR , do not take it. If you have a history of hepatitis B infection, kidney or liver issues, or are over 65 years old, tell your doctor. While using XAPAVIR , get blood and urine tests done on a regular basis. XAPAVIR does not prevent the transmission of HIV infection, therefore practice safe sex and take all essential measures. If you are pregnant or intend to become pregnant, speak with your doctor. XAPAVIR should not be taken during nursing. XAPAVIR can make you dizzy, so drive carefully. Children under the age of 12 should not consume XAPAVIR . If you see any signs or symptoms of infection or inflammation, contact your doctor right once.
Interactions Between Drugs
HIV / PREP MEDICATIONS may interact with anti-HIV (ritonavir, darunavir), anti-fungal (amphotericin B), anti-viral (foscarnet, ganciclovir, cidofovir), antimicrobial (pentamidine), antibiotic (vancomycin), and anti-cancer (ritonavir, darunavir) (interleukin-2).
No drug-food interactions have been discovered or established.
HIV/ PREP MEDICATIONS MAY INTERACT WITH KIDNEY AND LIVER PROBLEMS.
Safety Suggestions
ALCOHOL
It is unknown if HIV / PREP MEDICATIONS interacts with alcohol in any way. Please seek medical advice.
PREGNANCY
If you have any concerns, please visit your doctor; your doctor will only prescribe if the benefits outweigh the dangers.
BREAST FEEDING
If you’re taking HIV / PREP MEDICATIONS, don’t breastfeed since it may enter into your milk.
DRIVING
DIzziness is a side effect of HIV / PREP MEDICATIONS. As a result, only drive or operate machinery if you are aware.
LIVER
It’s possible that you’ll need to modify your dosage. If you have a liver condition or have any concerns, please check your doctor before using HIV / PREP MEDICATIONS.
KIDNEY
It’s possible that you’ll need to modify your dosage. If you have renal impairment or have any concerns, please see your doctor before using HIV / PREP MEDICATIONS.
No habit formation
Advice on Diet and Lifestyle
Use condoms for safe sex; it helps to reduce contact with semen and vaginal secretions.
Razor blades and toothbrushes, for example, should never be shared since they may contain bodily fluids or blood.
Sharing used needles, other injection or drug equipment is not a good idea.
Other sexually transmitted illnesses, such as gonorrhoea and syphilis, might make you more susceptible to HIV infection.
Consume a nutritious and well-balanced diet. Boost your immune system by eating vitamin and nutrient-rich foods including dark-green, yellow, orange, and red vegetables and fruit. Lean protein and nutritious carbohydrates are the best choices.
Raw meat and eggs should be avoided. Consume meat, poultry, or seafood that has been properly boiled and prepared.
If you’re experiencing nausea or vomiting, stick to bland, low-fat diets and stay away from spicy or greasy foods.
Spend time with relatives or do whatever makes you happy to relieve mental and physical stress.
Recommendations
Get an HIV test at least once every three months.
While using HIV/ PREP MEDICATIONS, it is recommended that you get regular kidney and liver function testing, as well as a bone mineral density test.
Because HIV / PREP MEDICATIONS may alter laboratory test results, tell the person doing the testing that you are taking them.
Additional Information: This item is non-refundable.
Glossary of Diseases and Conditions
HIV infection: HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that targets the immune system and kills white blood cells that assist the body fight infection, leaving the person vulnerable to additional infections or diseases. Flu-like symptoms include fever, chills, rash, night sweats, muscular pains, fatigue, and sore throat in HIV patients. These symptoms might persist anywhere from a few days to many weeks. HIV is transmitted by bodily fluids such as sperm, vaginal discharge, and blood. This illness can progress to AIDS if left untreated (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome). It is a chronic illness for which there is no known cure. It can, however, be treated with antiretroviral medications to keep it under control.
FAQs
Stopping HIV / PREP MEDICATIONS without contacting your doctor may impair the efficacy of antiretroviral treatment. Continue to use HIV / PREP MEDICATIONS for as long as your doctor has given them in order to effectively treat your disease. If you have any problems while using HIV / PREP MEDICATIONS, don’t be afraid to talk to your doctor.
lactic acidosis (excess lactic acid in the blood) is an uncommon but serious adverse effect of HIV/prep medications, especially in obese women and individuals with liver illness. If you have stomach discomfort, vomiting, nausea, sleepiness, or rapid deep breathing while taking HIV / PREP MEDICATIONS, see a doctor right away.
PREP MEDICATIONS for HIV do not cure the virus. HIV / PREP MEDICATIONS, on the other hand, can assist to reduce the risk of acquiring AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) and other HIV-related illnesses including cancer or dangerous infections.
If recommended by a doctor, HIV / PREP MEDICATIONS can be used by HIV negative persons to reduce their risk of contracting HIV. You should have a negative HIV test before commencing treatment, and you should have frequent HIV testing for at least every three months while taking HIV/ PREP MEDICATIONS.
MEDICATIONS FOR HIV/AIDS PREVENTION (HIV/AIDS PREVENTION) MAY CAUSE BONE PROBLEMS, such as soft bones, thin bones, and bone pain. When using HIV/ PREP MEDICATIONS, a regular bone density test is recommended. Take calcium and vitamin D supplements as directed by your doctor for optimum bone health.




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.